Curriculum
An overview of the main curricula offered at international schools in Malaysia.
Differences Between Japanese and Malaysian Education Systems
As interest in parent-child study abroad and mother-child study abroad in Malaysia increases, how many people are familiar with Malaysia’s education system? Did you know that Malaysia actually offers more educational options than Japan?

In Japan, compulsory education consists of 6 years of elementary school and 3 years of junior high school, totaling 9 years, and all children are required to receive this compulsory education. After completing compulsory education, most students proceed to high school, but high school education is not mandatory and is optional. Post-secondary options include 4-year universities, junior colleges, and vocational schools, and students choose based on their career paths. Students aiming for university prepare for entrance exams through their high school studies.
However, in Malaysia, compulsory education is 6 years of Primary School. However, unlike Japan, this is not mandated by law and can be adjusted according to family circumstances. After completing primary school, there are 5 years of Secondary School (equivalent to junior and senior high school), after which students take the unified examination (SPM: Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia). Based on SPM results, students can proceed to pre-university programs, vocational schools, or directly to universities. While there are many domestic universities in Malaysia, it is also common to proceed to partner universities overseas. Many students aim for internationally recognized universities and vocational schools abroad.
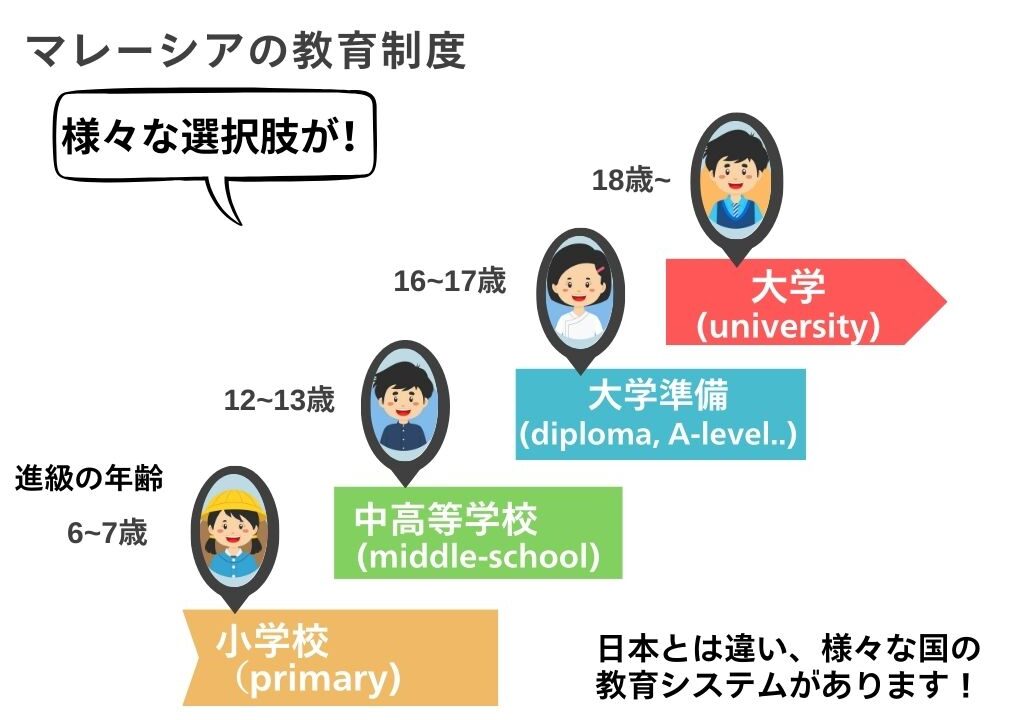
As you can see, there are differences between the Japanese and Malaysian education systems, and Malaysia can be considered to have more freedom and choices. After understanding these differences, let’s take a closer look at Malaysia’s education system.
About International Schools
Currently, there are over 170 international schools in Malaysia. In fact, international schools in Malaysia use different curricula from public schools, and even though they are all called international schools, each school implements different educational methods. Each school has its own unique characteristics in terms of the type of curriculum offered and the qualifications available. Therefore, choosing which international school to attend is an important decision. International school curricula are broadly divided into five types: British, American, Australian, Canadian, and International Baccalaureate. When choosing an international school, it is important to understand the characteristics of each curriculum. The British curriculum is particularly the most popular curriculum at Malaysian international schools. However, some schools offer multiple curricula and qualifications, such as starting with an American curriculum and offering the International Baccalaureate (IB) at the pre-university level. The international curricula offered in Malaysia are diverse, with over 10 types of curricula and examinations available.

Curriculum Comparison Table
| Category | British Curriculum | IB (International Baccalaureate) | American Curriculum | Australian Curriculum | Canadian Curriculum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Features | One of the most widely adopted international education systems in the world. Systematic with high academic standards, strong in logical thinking and exam preparation. | Emphasizes international perspective, inquiry-based learning, and holistic education. Develops multicultural understanding and independence. | Flexible with many elective subjects, emphasizing individuality and creativity. Diverse assessment methods. | Emphasizes practical and collaborative learning. Many research, presentation, and experiential lessons. | Based on provincial education standards (especially Ontario), emphasizing critical thinking and social skills. |
| Grade Structure | Nursery to Year 13 (13 years) Primary (Year 1-6) Secondary (Year 7-11) Sixth Form (Year 12-13) | PYP (ages 3-12) MYP (ages 11-16) DP/CP (ages 16-19) | Elementary (Grade 1-5) Middle (Grade 6-8) High (Grade 9-12) | Foundation to Year 12 (13 years) Primary (Year 1-6) Secondary (Year 7-12) | Elementary (Grade 1-8) High School (Grade 9-12) |
| Terms | 3 terms (September, January, April) | 2 semesters (August/September start, January second semester) | 2 semesters (August/September start) | 4 terms (January, April, July, October start) | 2 semesters (September start, January second semester) |
| Assessment | Regular exams + assignments. GCSE/IGCSE for grades, A-Level for university preparation. | Internal assessment (homework, essays, extracurricular activities) + global standardized exam (DP unified exam). | Tests 50-70% + assignments 30-50%. GPA system. | Comprehensive evaluation of tests, assignments, presentations, and projects. | Grade evaluation (Assignments + Exams + Projects). Based on OSSD criteria. |
| Graduation Qualifications | IGCSE (Year 11) A-Level (Year 13) | IB Diploma (upon DP completion) | High School Diploma + SAT/ACT scores | Australian Certificate (SACE/WACE/VCE, etc.) | OSSD (Ontario Secondary School Diploma) |
| University Pathways | Widely recognized in UK, Australia, Singapore, etc. | Highly valued by universities worldwide (including UK, US, Japan). | Suitable for US and Canadian university admission. | Strong for Australian and New Zealand universities. | Strong for English-speaking universities including Canada, UK, and Australia. |
| Representative Schools (KL) | Alice Smith, Garden Int’l, Epsom College | IGB Int’l, Mont’Kiara Int’l | ISKL, Mont’Kiara Int’l | Australian Int’l School Malaysia (AISM) | Sunway Int’l School |
| Educational Philosophy Keywords | Exam-focused, logical, systematic | Inquiry, international understanding, critical thinking | Freedom, creativity, flexibility | Practical, collaborative, balanced | Social skills, critical thinking, multicultural understanding |
| Difficulty (General Assessment) | 4/5 stars (Academic) | 5/5 stars (Comprehensive, challenging) | 3/5 stars (Flexible) | 3/5 stars (Practical) | 4/5 stars (Balanced) |
British Curriculum
Features
Based on the National Curriculum
Many British-style international schools adopt the English National Curriculum and British qualifications (IGCSE, A-Level, etc.) as their foundation.Wide Range of Subjects and Freedom of Choice
At the primary level, students learn a wide range of subjects, and as they progress, elective subjects increase, allowing students to focus on their specializations and interests.Clear Assessment System and Certification Exams
Many schools have adopted internationally recognized examination systems such as GCSE/IGCSE and A-Level (or equivalent examination systems).University Pathway Preparedness
British programs are highly compatible with university entrance requirements in the UK, Europe, Asian countries, and many other countries, making the pathway to university relatively clear.Structured System and Easy Transitions
Following the Key Stage system, learning is set up in stages, making it easier to design learning according to students’ developmental stages.
Grade Structure
The British curriculum generally follows these divisions:
| Division | Age/Grade Equivalent | Content/Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Early Years / Foundation / Reception | Approximately 3-5 years old | Kindergarten and foundational education stage. Education that combines play and learning. |
| Key Stage 1 | Ages 5-7 (Year 1-2) | Acquisition of basic knowledge and skills in English, Mathematics, basic Science and Social Studies, etc. |
| Key Stage 2 | Ages 7-11 (Year 3-6) | Learning a wider range of subjects and consolidating basic academic skills. |
| Key Stage 3 | Ages 11-14 (Year 7-9) | Deepening learning and broadening the range of subjects toward secondary education. |
| Key Stage 4 | Ages 14-16 (Year 10-11) | The year for IGCSE/GCSE examinations. Narrowing down subject choices. |
| Key Stage 5 / Sixth Form | Ages 16-18 (Year 12-13) | Taking A-Level or equivalent exams (or university preparatory subjects). Preparation for university entrance. |
Additionally, many British-style international schools incorporate supplementary programs (extracurricular activities, inquiry-based learning, etc.) in addition to the Key Stage structure above.
Terms
Many British-style international schools adopt a 3-term system, although some schools use a 2-term system.
Main divisions:
Autumn Term: September to December
Spring Term: January to March/April
Summer Term: April to June/July
However, start and end dates and holiday schedules vary by school and region.
Enrollment timing: Generally September enrollment is primary, but January enrollment (transfer from Term 2) is accepted by some schools.
Assessment
Assessments are conducted at the end of each Key Stage or at intermediate stages to confirm progress and achievement.
IGCSE/GCSE Examinations: External certification exams are taken at the end of Key Stage 4, with grades awarded for each subject.
A-Level: Elective subjects are taken in Key Stage 5 (Sixth Form), and final exam results are directly linked to university admissions.
Grades are often shown by grade evaluation (A*, A, B, C… etc.) for each subject.
Assignments and internal assessments (school exams, quizzes, assignment submissions, projects, etc.) are also incorporated into grade evaluation.
Graduation Qualifications
IGCSE/GCSE Qualifications: Obtaining these is important as intermediate achievement certification in British-style education. They may also become basic requirements for university admission.
A-Level (or equivalent exam): The highest-level exam in British-style international schools. A-Level results play a major role in university admissions.
Many British-style schools provide career guidance focused on university admission based on A-Level results.
Many universities in the UK, Europe, Asia, Australia, and other countries accept A-Level as an evaluation criterion.
School Directory
Schools in Kuala Lumpur (KL)
| School Name | Overview |
|---|---|
| The British International School of Kuala Lumpur (BSKL) | Offers English National Curriculum / IGCSE / A-Level. From early childhood to Sixth Form. |
| Alice Smith School | Non-profit British-style international school. British curriculum education for ages 3-18. |
| Garden International School (GIS) | One of the prominent schools adopting the British curriculum. Ages 3-18. |
| Epsom College in Malaysia | School implementing British curriculum / A-Level, etc. From kindergarten to high school level. |
| King Henry VIII College | School offering British curriculum. From early childhood to high school. |
Schools in Penang
| School Name | Overview |
|---|---|
| Prince of Wales Island International School (POWIIS) | Offers British system (IGCSE & A-Level). Ages 3-18. Has boarding facilities. |
| Tenby Schools Penang | Has a British International School division offering British curriculum including IGCSE. Early childhood to secondary education. |
| Stonyhurst International School Penang | Primarily English National Curriculum, offering IGCSE/A-Level. Primary to secondary to Sixth Form. |
| Straits International School Penang | Implements British curriculum (IGCSE, etc.) for primary and secondary education. |
| BXCL International School Penang | Offers British-style education from early childhood to age 18. School with Pre-University stage (A-Level, etc.) options. |
Schools in Johor Bahru
| School Name | Overview |
|---|---|
| Tenby Setia Eco Gardens, Johor Bahru | Tenby group school. Offers international/British-style primary to secondary education. |
International Baccalaureate (IB)
Features
An international education program headquartered in Switzerland, established in 1968, emphasizing multifaceted perspectives, international leadership, and holistic education.
Education aimed at developing not only academic ability but also “thinking skills,” “inquiry mind,” “creativity,” and “sociality.” Project-based learning, inquiry-based learning, and practical activities (creativity, activity, service, etc.) are required.
Emphasizes cultivating cross-cultural understanding and global mindset. Highly recognized by universities in various countries and often valued for university admission purposes.
Program Structure
IB has mainly four programs. They are structured according to students’ age and developmental stages.
| Program Name | Target Age/Grade | Overview |
|---|---|---|
| PYP (Primary Years Programme) | Approximately ages 3-12 (primary education) | Centered on inquiry-based and thematic learning, studying language, mathematics, science, arts, etc. in a cross-curricular manner. Develops children’s independence, observation, thinking, and inquiry abilities. |
| MYP (Middle Years Programme) | Approximately ages 11-16 (lower/middle secondary education) | Develops practical and critical thinking through multi-subject learning and individual projects. Interdisciplinary Units are also introduced. |
| DP (Diploma Programme) | Approximately ages 16-19 (2 years of high school) | Program for university preparation. Includes subject selection and core subjects (TOK, EE, CAS), evaluated through external exams and internal assessment. |
| CP (Career-related Programme) | Approximately ages 16-19 | Program combining career-related education (career-oriented) with academic education. Consists of DP subjects + career-related subjects. |
Terms
The term system varies by country and school, but IB schools generally adopt a two-semester system, first/second half, or some also adopt a tri-semester system.
The new term (first half) generally starts in August or September, with the second half being January or later. Some schools accept transfers from the second semester.
Assessment
Each program (DP, MYP, CP) uses both Internal Assessment and External Assessment, with different assessment methods for each subject.
For example, in DP, subject examinations (written exams, etc.) + assignments/essays (EE: Extended Essay, TOK: Theory of Knowledge) + CAS (Creativity, Activity, Service) are required. EE and TOK include external/internal assessment.
Grades are evaluated on a 1-7 scale for most subjects (7 being the highest). Points are totaled by subject, and in DP, diplomas are awarded to those who meet the minimum score requirements.
In MYP, course results and certificates may be certified through formats such as eAssessment. There is a system for reflecting on students’ learning and progress by mixing internal and external assessments.
Graduation Qualifications
By completing the DP (Diploma Programme), the IB Diploma is awarded. Having this diploma is a major advantage for university admission.
To obtain the DP Diploma, several requirements must be met:
Select 6 subjects and obtain grades for each (7-point scale)
Complete and be evaluated in the 3 core subjects: TOK (Theory of Knowledge), EE (Extended Essay), and CAS
Meet the minimum total score requirement (24 points, etc.) (with additional conditions such as minimum levels for each subject)
MYP, CP, and PYP may also have completion certificates (although PYP emphasizes learning progress and ability development rather than formal transcripts)
School Directory
Schools in Kuala Lumpur (KL)
| School Name | IB Programs Offered / Notes |
|---|---|
| The International School of Kuala Lumpur (ISKL) | Offers IBDP. Ages 3-18. Full IB curriculum (DP) authorized school. |
| Mont’Kiara International School (M’KIS) | Offers PYP, MYP, DP (continuous IB curriculum). |
| IGB International School (IGBIS) | Offers PYP, MYP, DP (continuous IB curriculum). |
| Fairview International School (KL campus) | Wangsa Maju campus and others, offering IB programs including PYP to DP. |
| Nexus International School | Combined IB + British curriculum school. IB programs including DP available. |
Schools in Penang
| School Name | IB Programs Offered / Notes |
|---|---|
| The International School of Penang (Uplands) | PYP, MYP, DP continuous IB program (IB Continuum). From early education to graduation. |
| Fairview International School Penang | Offers PYP and MYP. Wide age range, IB program authorized school. |
| Stonyhurst International School Penang | Option to select IB Diploma alongside A Levels at Sixth Form (high school). |
Schools in Johor Bahru
| School Name | IB Programs Offered / Notes |
|---|---|
| Fairview International School Johor Bahru | Offers PYP and MYP. |
American Curriculum
Features
Flexibility and Emphasis on Individuality
The American system emphasizes “student-centered” education, featuring a flexible structure that allows students to select subjects according to their individual interests and abilities.
Assessment methods are also multifaceted, with emphasis on presentations, group work, and Project-Based Learning in addition to tests.Developing Thinking and Creativity
The educational approach develops “the ability to think for oneself and express opinions” rather than rote memorization. With many discussions and research assignments, it develops the critical thinking needed after university admission.Introduction of AP (Advanced Placement) Subjects
At the high school level, many schools offer “AP programs (university-level classes),” and excellent grades may be recognized as university credits in the US and other countries.
Some schools allow students to choose alongside the IB Diploma (International Baccalaureate DP).Preparedness for Global University Admission
The American curriculum is highly recognized by universities worldwide, meeting university entrance requirements in the US, Canada, Japan, UK, Australia, and many other countries.
Grade Structure
The American system is based on the “K-12 education system (Kindergarten to Grade 12)” and is divided into the following three stages.
| Education Stage | Grade | Approximate Age | Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elementary School | Grade 1-5 | Approximately 6-11 years old | Acquisition of basic academic skills. Reading, mathematics, social studies, science, etc. Inquiry-based learning is also introduced. |
| Middle School | Grade 6-8 | Approximately 11-14 years old | Broadening academic scope and strengthening presentation and research skills. Many club activities. |
| High School | Grade 9-12 | Approximately 14-18 years old | University preparation. AP and IBDP course selection available. Volunteer work and extracurricular activities are also evaluated. |
Terms
General Term System: 2-Semester System
1st Semester (Fall Semester): August/September to December
2nd Semester (Spring Semester): January to May/June
*Some schools adopt a Trimester System (3 terms).
Transfer Timing
Basically August/September enrollment, but many schools accept January enrollment (transfer from 2nd semester), making it easy to accommodate transfer students from overseas.
Assessment
| Assessment Method | Ratio (Approximate) | Content |
|---|---|---|
| Exams/Tests | Approximately 50-70% | Regular exams, unit tests, etc. |
| Assignments/Reports/Labs | Approximately 20-30% | Inquiry assignments, research reports, group work |
| Class Attitude/Attendance/Presentations | Approximately 10-20% | Daily participation attitude and presentations, etc. |
Grades are managed using A-F evaluation (GPA system), and GPA averages are emphasized during university applications.
GPA (Grade Point Average) generally uses a 4.0-point scale (e.g., A=4.0, B=3.0, C=2.0, etc.).
Graduation Qualifications
High School Diploma
A qualification awarded when students meet each state’s or school’s credit requirements. This becomes the basic qualification for university applications.
(e.g., 4 credits of English, 3 credits of Mathematics, 3 credits of Science, 3 credits of Social Studies, 1 credit of Arts, etc.)External Exams for University Admission:
SAT (Scholastic Assessment Test): Standard test for US university admission.
ACT (American College Testing): Similarly for university admission. Equivalent to SAT.
TOEFL / IELTS: Those from non-English-speaking countries need to submit English proficiency test scores.
AP Exams: May be recognized as university credits.
University Admission Results:
Students can proceed not only to US universities but also to many universities in Canada, UK, Australia, and Japan.
Especially the combination of U.S. High School Diploma + SAT/ACT is a globally recognized standard qualification.
School Directory
| Region | School Name | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Kuala Lumpur / Selangor | – The International School of Kuala Lumpur (ISKL) – Mont’Kiara International School (M’KIS) – The American School of Kuala Lumpur (ISKL) | All American-style based. AP courses offered. High university admission results. |
| Penang | – Dalat International School | Traditional American-style international school. AP subjects available, Christian-affiliated. |
| Johor Bahru | – Marlborough College Malaysia (fusion with British style) – Austin Heights International School (American-British mixed) | Flexibly accommodates both American and British university pathways. |
Australian Curriculum
Features
Adopts curriculum certified by the Australian Department of Education (primarily New South Wales or Victoria).
The focus of learning is on “inquiry, thinking, presentation, and collaboration.”
Emphasizes understanding, application, teamwork, and expression rather than memorization.Many teachers are from Australia, and all classes are conducted in English.
Respects each student’s individuality and emphasizes a low-stress, open educational environment.
Compared to Japanese or British styles, there is a stronger tendency toward “holistic education (academic + emotional development),”
with emphasis on developing students’ “sociality” and “leadership.”Uniforms and school culture are relatively friendly, with a homey atmosphere as a characteristic.
Grade Structure
Australian-style international schools in Malaysia
basically follow the same 13-year system (Foundation to Year 12) as Australia.
| Education Stage | Grade | Approximate Age | Content/Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Early Learning / Foundation | Preschool (Nursery to Kindergarten) | 3-5 years old | Learning English, numbers, and sociality through play. Foundation of inquiry-based learning. |
| Primary School | Year 1 to Year 6 | 6-12 years old | Comprehensive study of English, mathematics, science, social studies, arts, ICT, physical education, etc. |
| Secondary School | Year 7 to Year 10 | 13-16 years old | Specialized subjects increase, emphasizing critical thinking and problem-solving. Internal assessment at the end of the secondary program. |
| Senior Secondary (Pre-University) | Year 11 to Year 12 | 16-18 years old | Study toward obtaining state-recognized university qualifications (VCE or HSC). |
Terms
Adopts a January start, 4-term system.
The year is divided into four terms, with approximately 2 weeks of vacation between each term.
| Term | Period (Approximate) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Term 1 | Late January to late March | New school year begins |
| Term 2 | April to June | Mid-term assessment |
| Term 3 | July to September | Project-based learning focus |
| Term 4 | October to December | Year-end exams and assessment |
Mid-December to mid-January is summer vacation (long break).
The calendar in Malaysia is almost the same as in Australia.
Assessment
Not only regular exams but also daily assignments, participation attitude, and group work are emphasized.
Assessment balance is approximately:
Tests/written exams: 50-60%
Projects/presentations/reports: around 30%
Participation/attitude/assignment submission: 10-20%
Uses 5-level A-E evaluation or 100-point scale.
Grades are reported twice a year through “Progress Reports” and once a year through “Final Reports.”
Not only grades but also learning attitude, sociality, leadership, and thinking ability are comprehensively evaluated.
Graduation Qualifications
Depending on the school attended, students obtain one of the following state-certified qualifications.
| Curriculum | Graduation Qualification | State | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| VCE (Victorian Curriculum & Assessment Authority) | Victoria Certificate of Education | Victoria | Adopted by Peninsula International School Australia. |
| NSW Curriculum (New South Wales) | Higher School Certificate (HSC) | New South Wales | Adopted by Australian International School Malaysia. |
Both VCE/HSC are internationally recognized and valid as university admission qualifications worldwide.
The “ATAR (Australian Tertiary Admission Rank)” calculated from these final exam results is used for university admission reviews.
Direct admission to universities both in and outside Malaysia (Australia, UK, US, Japan, Singapore, etc.) is possible.
Malaysia has a campus of Monash University, a prestigious Australian university, and it is possible to obtain a Monash University degree while studying in Malaysia. This has become a popular university among Japanese students in recent years. This curriculum is recommended for students aiming for Monash University or other Australian universities.
School Directory
Schools Near Kuala Lumpur
| School Name | Overview |
|---|---|
| Australian International School Malaysia (AISM) | Ages: 3-18 (Preschool to Year 12) Curriculum: New South Wales “Australian Curriculum” and Higher School Certificate (HSC). Features: Incorporates Visible Learning. Relatively small class sizes and international community. Annual tuition is approximately MYR 40,000-80,000. |
| Peninsula International School Australia (PISA / Malaysia branch) | Ages: 4-18 (Early Years to Secondary) Curriculum: Victoria State “Australia Victoria Curriculum” Graduation Qualification: Offers Victoria Certificate of Education (VCE). |
Canadian Curriculum
Features
Adopts the Canadian provincial government (primarily Ontario) education curriculum.
→ Some schools are officially certified by the Ontario Ministry of Education.Educational philosophy is “Inquiry-Based Learning” and “Holistic Education.”
Emphasizes not only academic ability but also the development of sociality, ethics, and communication skills.Emphasizes understanding, application, and presentation skills rather than rote memorization.
Develops students’ ability to think for themselves, express opinions, and solve problems collaboratively with others.Considers students for whom English is not their native language, with comprehensive ESL (English as a Second Language) programs.
Features a relatively calm, cooperative and warm school culture, with close relationships between teachers and students.
Equivalent curriculum content to Canadian public high schools, with graduates able to proceed to universities in Canada, America, UK, Australia, Japan, and more.
Grade Structure
The Canadian education system is 13 years (Kindergarten to Grade 12).
In Malaysia, it is structured as follows.
| Education Stage | Grade | Approximate Age | Content/Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kindergarten | JK (Junior Kindergarten) to SK (Senior Kindergarten) | 4-5 years old | Getting used to the English environment, learning basic arithmetic, reading/writing, and sociality. |
| Elementary School | Grade 1 to Grade 6 | 6-12 years old | Comprehensive study of English, mathematics, science, social studies, music, art, etc. Thinking-focused lessons. |
| Middle School | Grade 7 to Grade 8 | 12-14 years old | Group work and project-focused. Developing presentation skills. |
| High School | Grade 9 to Grade 12 | 14-18 years old | Taking specialized subjects (mathematics, science, economics, IT, literature, etc.) with university in mind. |
Terms (School Calendar)
Adopts a 2-Semester System.
The new school year starts in August or September and ends around June of the following year.
| Semester | Period (Approximate) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1st Semester (Fall Semester) | August to December | New semester begins. Term ends in December. |
| 2nd Semester (Spring Semester) | January to June | Final exams, grade advancement assessment. |
| Summer Break | Mid-June to mid-August | Some schools offer summer school. |
The academic calendar is almost the same as Canada, with Christmas break and March Break (spring vacation).
Assessment
The Canadian system features “emphasis on regular grades”, with importance placed on daily work as well as tests.
| Assessment Subject | Ratio (Approximate) | Content |
|---|---|---|
| Assignments/Reports/Presentations | Approximately 40-50% | Group work, essays, presentations, etc. |
| Exams (Midterm/Final) | Approximately 30-40% | Written exams, listening, reading comprehension, etc. |
| Participation Attitude/Attendance/In-class Activities | Approximately 10-20% | Proactivity, cooperation, and learning attitude are also evaluated. |
Evaluation is shown as A-F (or 100-point scale).
70% or above is the passing line.
Each subject also separately evaluates Learning Skills (study attitude).
Report Cards are issued twice per term.
Regular Parent-Teacher Conferences are also held.
Graduation Qualifications
Canadian-style international schools mainly award the Ontario Secondary School Diploma (OSSD).
Requirements for obtaining OSSD:
Earn 30 or more credits (required + elective subjects)
Complete 40 or more hours of volunteer activities
Pass the provincial standardized test (Ontario Secondary School Literacy Test)
OSSD is recognized as an official admission qualification by universities worldwide.
Within Malaysia, it is also possible to proceed to Sunway University or Monash University Malaysia.
High university admission rates to Canada, US, UK, and Australia, making it popular with families oriented toward North America.
Canadian-Style International Schools in Malaysia
| Region | School Name | Main Features |
|---|---|---|
| Kuala Lumpur (KL) | Sunway International Schools (Sunway City KL campus) | Covering Kindergarten to Secondary to Pre-University, offering Ontario (Canadian province) curriculum. Ontario Ministry of Education certified teachers also on staff. |
| Johor Bahru (Iskandar) | Sunway International Schools (Sunway City Iskandar Puteri campus) | Similarly offers Ontario curriculum. Primarily adopts Ontario for Kindergarten/Primary stages. |
| Johor Bahru (Taman Desa Tebrau) | Maple International School | Offers IGCSE & CPU (Canadian Pre-University) programs. A school where you can select “CPU” as a Canadian-style Pre-University course. |
